Post Go-Live Best Practices
Credit and A/R projects are large, complex, expensive and fraught with risks. This e-book demystifies technologies such as Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence to help finance leaders transform operations.
Post Go-Live Best Practices
Post go-live it is all about evaluating the new processes and applying course corrections as and when required.
Evaluate KPIs
Process owners have to revisit KPIs and check whether TO-BE processes that were designed in the audit phase are performing to expectations. Figure 16 shows possible steps needed depending on whether performance of the new system meets expectations or not. 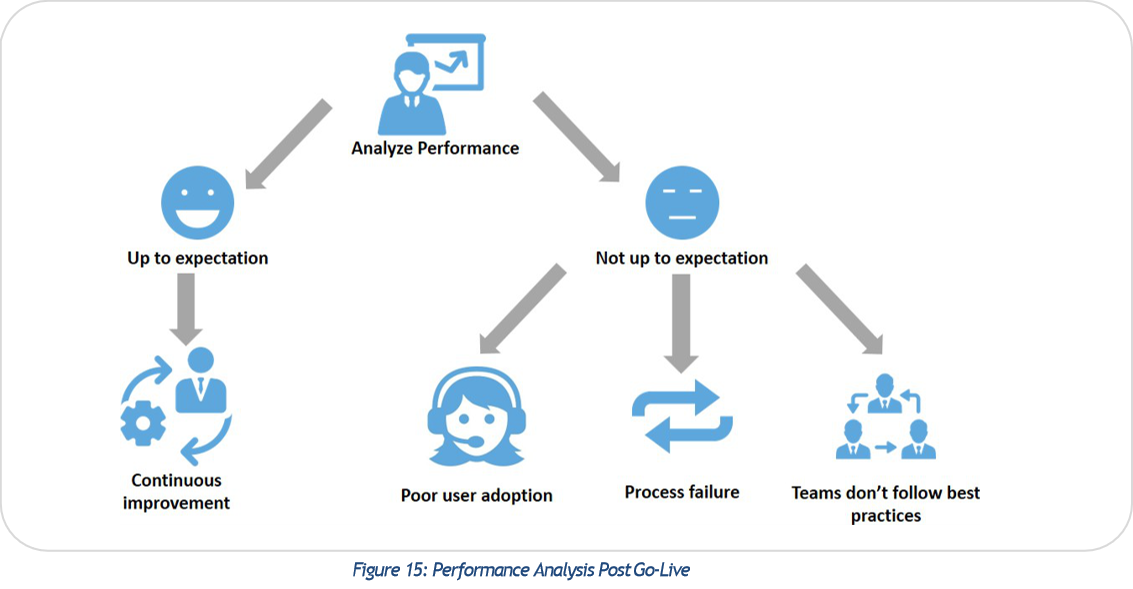 If the implementation performs as expected, set these processes for a continuous improvement program for yearly gains. If the performance is not up to expectations, do a root cause analysis and fix the problems. It has been found that most failures mainly fall into three buckets:
If the implementation performs as expected, set these processes for a continuous improvement program for yearly gains. If the performance is not up to expectations, do a root cause analysis and fix the problems. It has been found that most failures mainly fall into three buckets:
- User adoption: Poor user adoption is a big factor in process failure for improvements but is only apparent when users start affecting the processes through adoption
- Failure to adhere to best practices: This is also another major factor in failure as each process has a set of best practices to follow for maximum impact
- Poor process design: This scenario is not as frequent as the above two but could happen if the process designed was not up to the mark
Apply Course Corrections
Once root-cause analysis has been completed, decide on course corrections. Figure 17 – Steps to correct failures related to user adoption, stabilization and ways to monitor performance. 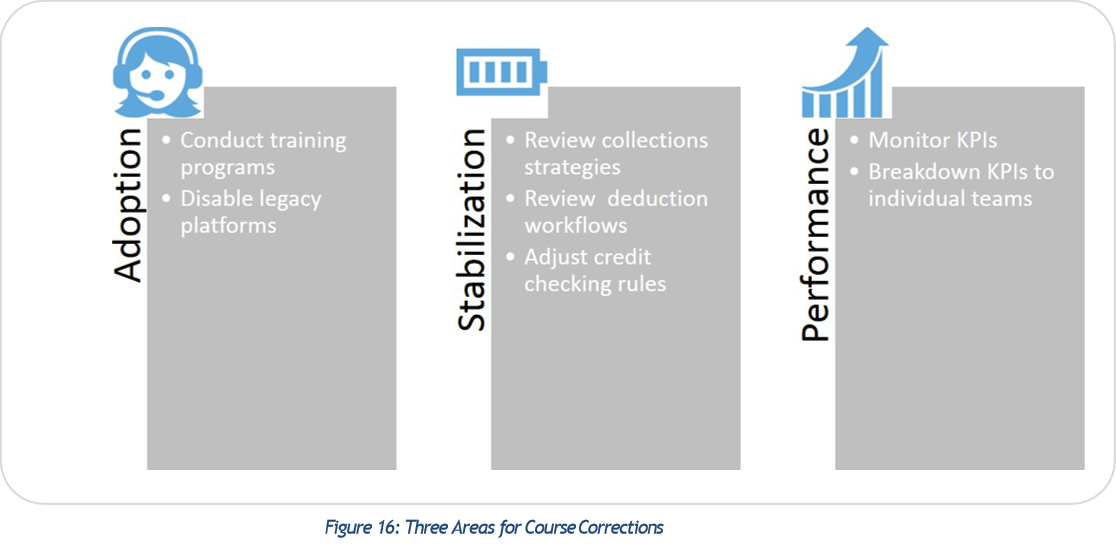 User adoption and adherence to best practices are improved by conducting training programs and disabling access to legacy platforms. Breaking down KPIs to individual teams will also help in a comparative analysis of where each team stands. Addressing process design failure means credit and A/R teams must ?go back to the drawing board? to redesign the process. A system will only be as good as the inherent process that runs on it. Some of the common processes that need reviewing are 1) Credit workflows, 2) Collections strategies and collections segments, 3) Dispute resolution workflows, and 4) Cash Application process.
User adoption and adherence to best practices are improved by conducting training programs and disabling access to legacy platforms. Breaking down KPIs to individual teams will also help in a comparative analysis of where each team stands. Addressing process design failure means credit and A/R teams must ?go back to the drawing board? to redesign the process. A system will only be as good as the inherent process that runs on it. Some of the common processes that need reviewing are 1) Credit workflows, 2) Collections strategies and collections segments, 3) Dispute resolution workflows, and 4) Cash Application process.
