Shared Service Centre 2.0 | 3 Step Framework to Build Next-Gen Global Innovation Centers
- Order-to-Cash Shared Service Centres have evolved into GICs offering a technologically advanced workforce generating insights for the leadership team and core business
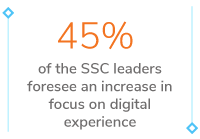
- 45% of the global Shared Service Centre leaders foresee an increased focus on digital experience and AI-driven automation
- Advanced digital technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and blockchain will drive the future of Order-to-Cash Shared Service Centres
Shared Service Centres Evolution From ‘Back Office’ to ‘Center
Evolution of SSCs to Global Service Centers
For long, businesses have used Shared Service Centers (SSCs) to achieve cost and operational efficiencies for managing back-end F&A or O2C processes related to customer payment processing, billing, credits, and collections, which were outsourced to process-specialized SSCs. The traditional F&A SSCs worked in a siloed environment with separate business objectives and processes, which restricted the exchange of information. For example, credit management might be separated from collection-related processes involving collections, deductions, and disputes. This resulted in complex and often opaque systems that did not facilitate communication between various processes and even sub-processes within the same process.
As SSCs gained popularity, their role started moving toward a co-located service center, wherein the entire O2C support across credit management, billing, payments, collections, and reconciliation was managed from a central location. However, O2C SSCs mainly handled targeted tasks and were not adding any value to the core business, such as assisting the sales team for potential customer leads with their credit risk evaluation. Also, there was less focus on process innovation, automation of workflows, and generating real-time insights, and the main activities only included standardization of the ongoing processes, leading to the commoditization of business processes. This in turn impacted the business growth, as the focus remained on cost optimization of the process from the process rather than designing better products or increasing sales, or exploring new markets.
Unlike the SSC model, where Shared Services Center is a separate entity that has emerged from core organization and that is responsible for providing services to its local business units, the GBS model consists of setting up a global, integrated and centralized organization that provides comprehensive and complex end-to-end processes (whereas in case of SSC, local business units continue to participate in process execution, as only some of clearly defined activities are transferred and consolidated in SSC).
Emergence of Global Innovation Centers that Generate Business Value


payment risk of customers. This becomes possible through a centralized service delivery. A GBS that could enable intercommunication between the processes could generate real-time insights for business leaders. This resulted in the adoption of Global Innovation Centers (GICs), providing an environment where processes no longer work in silos, and a workforce, which is technologically advanced to proactively answer business queries. This enables the innovation teams to support their organization’s overall strategy, including new idea generation and execution, improvement of customer experience, responses to immediate business requirements, real-time insights, and revenue generation. For example, the collections and credit teams can work in collaboration to provide information on credit risk, credit history, and history of blocked orders to the sales team for approaching potential customers and speeding up the onboarding of new customers.

revenue generation. For example, the collections and credit teams can work in collaboration to provide information on credit risk, credit history and history of blocked orders to the sales team for approaching potential customers and speeding up the onboarding of new customers.
Linda from Uber highlights that SSCs have evolved in terms of the type of support they have been providing. They are working in collaboration with business partners (FTEs of the parent company) to provide recommendations for business decisions and to determine the best practices for the business as they are involved in the day-to-day tasks. This has become possible mainly through the adoption of various digital technologies.
Adoption of Automation and Digital Technologies Driving the Future of Order-to-Cash Shared Service Centres
Moustapha from Bristol-Myers Squibb highlights that SSCs have evolved over time to enable innovation with the help of adopting technology in the cash application process. However, there is always a scope for improvement, e.g., enhancements in the efficiency of the treasury department, credit department, or the overall financial health of the company. Technology has the potential to offer customized solutions for specific processes or sub-processes, e.g., it can be used to run a real-time cash application process and bring the process at par with any other process in an organization.

existing ones. But the transformation also increases the interaction among the processes, both in volume and complexity. This is where automation techniques are needed to reduce the cost of labor and to make intelligent decisions. Tammy from Martin Marietta highlights that it is important to have an automation approach so that resources can be utilized effectively.
process. Innovative solutions adopted by shared services leverage technology to provide scalable and repeatable solutions, for example:
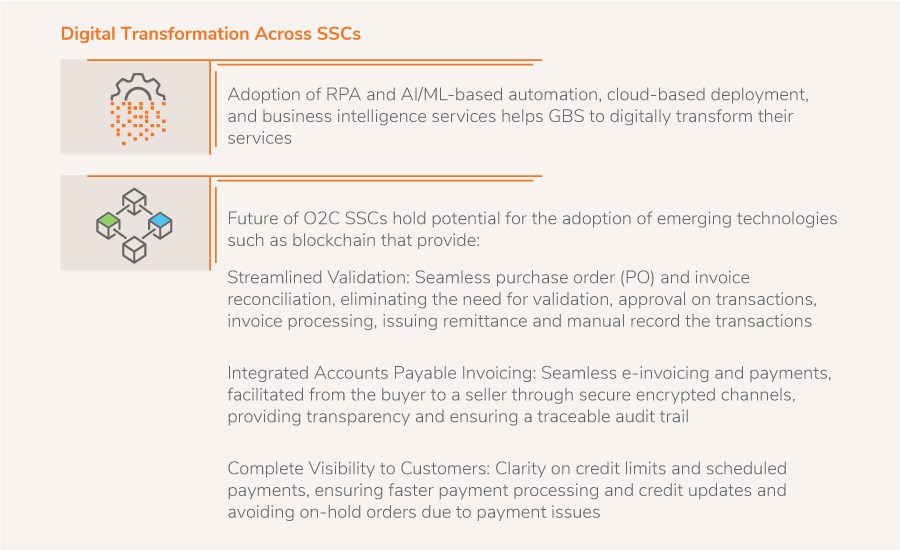
- Automation of the accounting processes facilitates resource efficiencies that can be channeled toward business development initiatives. As more transactions are automated, SSCs deal with limited service areas such as account payables and receivables. Also, automating paper-based work such as invoices and purchase orders, reduces the sheer volume of paper used, which when accompanied with reduced manual entry and reconciliation process, reduces the overall cost. In an account payable process, e-invoicing and automated matching of purchase order, delivery confirmation and vendor invoice eliminate the requirement of manual intervention. Key types of technologies being used for O2C processes are:
- Robotic Process Automation: To improve productivity, bots are deployed to take care of routine and repetitive tasks such as invoice entry, payment reminders, inventory database and balancing cash flow sheets, thereby avoiding delays in processing time and possible errors
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML techniques facilitate automated analysis and scanning of invoices, emails, and contracts, thereby reducing the manual effort. But the key application and value addition comes from the insights that it can generate with its analysis, that supports in decision making or taking automated intelligent decisions. For example, self-learning algorithms predict payment dates and identify risk of non-payment, and integrating this information across processes leads to relevant business insights
- Cloud-based deployment provides scalability and an environment for better operational integration across processes and ensures business continuity
- Business intelligence services for analyzing data and providing actionable insights affect strategic decisions

across accounting operations, making it easier for decision-makers to have end-to-end control of any changes in the existing processes. Future-ready businesses are adopting practices that combine human and machine intelligence, leveraging modular data and technology architecture with scalable processes, decision support teams, and agile front-end teams.

process. It provides complete visibility to all stakeholders in the O2C process. It increases the trust with the business leaders and helps in business decisions by providing real-time data such as credit information, buyer credit score, buyer payment behavior, payment history and validity of deductions claimed.
According to Tammy from Martin Marietta, digital transformation brings in process effectiveness and efficiency, and the ability to represent data so that it can be analyzed.
It is evident from the application of these emerging digital technologies that to adopt best-in-class practices and radically enhance the value generated from O2C processes, it is important to follow a digital approach.
The above eBook was just a glimpse out of an extensive Thought Leadership Whitepaper titled:
Future of Shared Service Centers for Order-to-Cash
Key Highlights of the Whitepaper
- SSCs for O2C have evolved to become a part of the core business operations and play a critical role in the overall digital transformation of businesses.
- 70% of digital transformations fail due to lack of discipline, visibility and tracking of business outcomes and KPIs.
- The best-in-class approach includes adopting digitization as a part of the DNA with continuous improvement and benchmarking.
- RPA was good while it lasted but the next generation technology is AI-native.
- Cloud-based integrated O2C platforms are digitally transforming SSCs.





