Winning Formula for Successful Digital Transformation in Shared Service Centres
- 70% of the digital transformation projects fail
- Leadership team is aware only of 4% of the finance issues
- Accurate assessment of the existing stage of digital maturity is the key to understand the right steps for digital transformation
- 90% of successful digital transformation is determined by organizational execution and only 10% by the technology deployed
Technology Adoption Does Not Guarantee Successful Digital Transformations - It Can Still Fail

guarantee a successful digital transformation. Businesses often overlook certain critical aspects of the transformation process, which could lead to considerable losses in terms of effort and investments. In fact, the ratio of the failure of digital transformations is as high as ~70%10.
O2C transformations can falter because of a number of reasons, some of which are as follows:
- Lack of Vision and Clarity: O2C reengineering and digitization have different meanings for different businesses. For some businesses, it could mean investing in AI to transform the accounts receivable process, or to optimize billing and invoicing in blockchain, while for others, digitization could simply be the usage of OCR to scan invoices. As Tony Saldanha (GBS expert and author of ‘Why Digital Transformations Fail’) suggests, lack of vision and clarity is one of the biggest reasons for the failure of digital transformation. To counter this, businesses need to build a complete roadmap of the transformation, which must include:
- Defining the meaning of digital transformation for each O2C activity, from credit management to cash application
- Setting up the parameters to measure the outcome of each O2C activity, such as the reduction in the risks involved in cash conversion cycles in cash conversion cycles, reduced sales outstanding, due percentage trends, disputes/deductions outstanding, reduction in the per order process cost, reduction in the sales outstanding number of days
- Analyzing customers’ needs and using them to make improvements in the overall O2C supply chain. For instance, the accounts payable digital initiatives of customers should not make the accounts receivable processes of the business more manual
- Aligning with the customer experience, because AP teams on the customer side are undergoing rapid digital transformation and the O2C digital initiatives should be able to help AR teams stay abreast. For example, if AP teams are focusing on invoice processing automation portals, then AR teams should ensure that they can seamlessly deliver and retrieve information to these portals
- Executional and Implementation Challenges: Some businesses, despite having a clear vision and understanding of the requirements, fail to execute them because of issues, such as:
- Inappropriate choice of platforms: Businesses often try to implement a fully-integrated O2C platform by uniting disjoint existing software within the company (integration of O2C with ERP, integration of predictive tools in customer servicing, etc.). It either results in the lack of integration between the different software packages, which typically need some manual effort, or will need an RPA bot to push files from one application to the other. In some cases, businesses end up with too much technology to manage
- Continuous deferring of O2C transformation: Because the integration of transformed O2C processes with legacy ERP systems is considered a challenge, businesses tend to defer the O2C transformation, fearing that they may need to upgrade their entire ERP solution. For this, businesses need to identify a transformation solution that is ERP system agnostic
- Organizational Readiness for Transformation: Decision-makers, such as the VP of Finance or the Head of GBS need to take up the ownership of making change management easy. This requires:
- Building front-end multifunctional teams because O2C processes span across many departments, including sales, marketing, contracting, and customer service. Also, it requires the O2C staff to be transversal and multifunctional in their skills
- Providing opportunities for horizontal upskilling – e-contracts and e-payments’ training for the AR team, and automation training for the sales staff that may choose to perform its tasks independently. O2C transformation has to be taken up as a business strategy initiative, which is why its implementation should go hand in hand with change management at the enterprise level
- Lack of Stakeholder Alignment in Organizations: In the corporate financial hierarchy, AR analysts11 are the ones aware of all of the (100%) of the problems with the financial processes. Managers get to know about three-fourths (74%) of the issues, while the leadership is aware of only 4% of the challenges. This warrants better alignment across the hierarchy by:
- Rolling out the projects in phases, starting with cash application to eliminate highly clerical, non-strategic work from the front line, followed by invoicing automation for seamless delivery and a digital customer experience, and followed by creating significant working capital impact by transforming strategic O2C processes like credit, collections and disputes and claims management
- Tracking the success metrics of the transformation during each phase, by considering feedback from the relevant stakeholders at each level, to refine the strategy of the next phase
- Lack of Foresight on Potential Market Disruptions: A competitive overview of the industry is imperative to counter potential disruptions, by keeping an eye on emerging technologies and ventures within, as well as outside the industry. Many upcoming technology startups are redefining O2C processes to make them more future ready. Some of those are the use of integrated e-signatures for payments and a cloud-based marketplace for invoice factoring, which allows buyers to provide an option of early payments to vendors. In terms of technology, blockchain can enhance O2C processes by providing increased visibility of purchase order attributes, such as shipping terms and late penalties, and payment receipt data, which in turn enhance the overall customer experience
To be successful, a guided, disciplined, and phased approach is required.

5 Phased Approach to Assess Digital Maturity
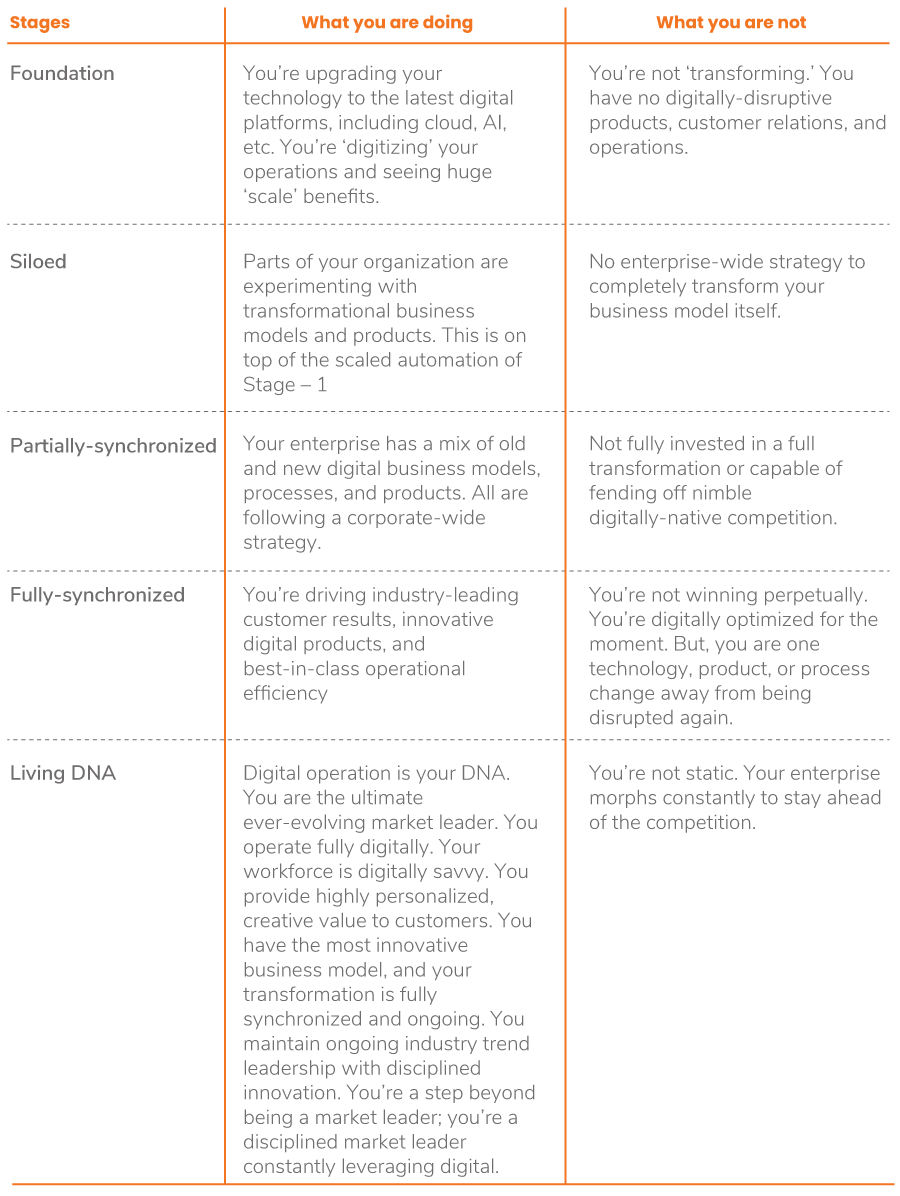
Before starting their digital transformation journeys, businesses need to develop a clear understanding of their existing levels of maturity with regard to the adoption of digital technologies. Tony Saldanha suggests that businesses can categorize themselves into one of five different stages of transformation. Accurate assessment of the existing stage can help a business take the right steps to digitally transform its O2C processes:
Digital Transformation 5.0 Model



Table Source: Why Digital Transformation Fail by Tony Saldanha

The Digital Toolkit for Shared Service Centres to Improve their Digital Maturity
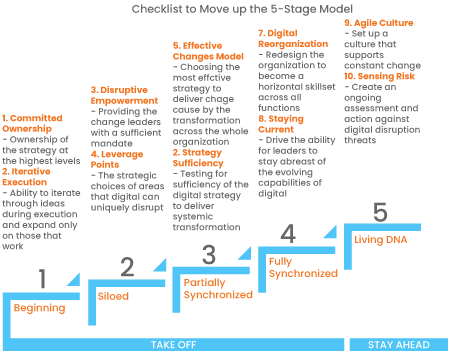
Checklist to Drive the Success Rate at Every Stage of Digital Transformation
Tony Saldana highlights that “there are very specific reliability drivers (and therefore checklists) to improve the success rate of each of the five stages of digital transformation.” He defined two disciplines or risk factors that are necessary for the successful delivery of each maturity stage. They are as follows:
-
Stage 1 – Beginning: Getting the Foundation Right
- Committed Ownership: To ensure that organization starts its journey for digital transformation, there is a need for a committed and dedicated AR and collection leadership to support this drive for innovation
- Iterative Execution: Exploring multiple ideas and expanding on ideas to generate business value (in terms of a gradual reduction in the number of O2C FTEs, error reduction in invoice scans, or efficiency achieved per order in terms of time and cost) in a phased manner
-
Stage 2 – Siloed: Taking Care of Processes in a Siloed Manner
- Disruptive Empowerment: Empowering individual O2C process owners to innovate and experiment within their scope of work
- Leverage Points: Identification of digital technologies that can be leveraged for individual processes (blockchain for invoicing for hassle-free customer payments, RPA for collections, or predictive analytics for credit management.) The O2C team should thoroughly analyze the availability of such business models, products, and technologies
-
Stage 3 – Partially Synchronized: Empowerment Across the Organization
- Effective Change Model: An effective change management plan, along with preparedness, which will address employees’ apprehensions regarding automation, aid the development of multifunctional front-end teams, and focus on enhancing customers’ experience during the early stages of change
- Strategy Sufficiency: Building a cross-departmental integrated strategy – unified focus on sales and order management, or an invoicing and payment strategy designed in conjunction with reporting and data management. This also paves the way for the next stage of developing an overall O2C strategy
-
Stage 4 – Fully Synchronized: Complete Digital Transformation
- Digital Re-organization: Digital re-organization and redesign are needed to build horizontal skills across functions, while also keeping in mind the existing capabilities. Other departments need to be trained for complexities around the sub-processes, customer disputes, short payments, lockboxes, payment terms, and AR teams in the data leverage capabilities from other departments
- Staying Current: Staying updated with evolving capabilities becomes important for continuous improvement in specific processes
-
Stage 5 – Living DNA: Embedding Innovation in Organizations’ DNA
- Agile Culture: Building a resilient and adaptable culture to adapt to technology changes by becoming system agnostic. For instance, O2C solutions should be ERP agnostic to avoid dependence on legacy systems. This also includes assessing threats, risks, and potential loopholes, and taking active steps to eradicate them
- Sensing Risk: Paying close attention to the disruptions that O2C transformation can cause to other functions. For example, O2C directly impacts sales, working capital, as well as the bottom line of a business
The checklist enables organizations to take care of the risk factors, based on the stage they want to leapfrog to. After assessing the stage of maturity and defining the risk factors, organizations need to work on becoming fully prepared to follow a phased framework for their digital transformation.
Toolkit for Digital Transformation
The six-step framework given below will assist organizations in prioritizing processes, selecting the transformative steps, and identifying the suitable technologies for a successful O2C transformation:
Setting the End Objective -> Assessing the Gaps in Current Processes -> Ideation of Solution -> Prioritization of Solution -> Building the Roadmap for Implementation -> Solution Pilot
- Setting Up the End Objectives: The transformation is often driven with at least one of the following objectives:
- Customer Experience-focused: End objective is to increase customers’ willingness to pay and improve retention rate by digitizing the customer experience
- Operation Efficiency-focused: End objective is to improve productivity and decrease cost by digitizing a part of the operations
- Customer Acquisition-focused: End objective is to attract new types of customers by digitizing the business model or changing the existing business model
Considering the complexity of the O2C operations, a clear end objective would make it easy to define the final roadmap. For instance, while having to decide between prioritizing an automated pull in a remittance advice system from pending payments or providing visibility across an O2C process, a customer-centric solution will favor the second option, while an operation-focused solution will prefer the first.
- As-is To-be Analysis:
- Process-level business goals and KPIs have to be defined. KPIs can be selected from average cycle times, average invoice to cash, DSO and ADD, percentage of unidentified payments, etc. Business goals should be defined (qualitative and quantitative) for each process individually and should match with the final objective. For example, order management goals could be to the extent of the turnaround of orders for operation focus, while it could be to the extent of visibility for CX focus
- Identifying the current status (as is) and achievable state (to be) – based on defined parameters and business goals – is critical, along with performing a gap analysis for each process
- Ideation: This step would build a use case from insights derived from a gap analysis:
- User and Customer-centric Immersion:
ii. Customers’ preferences need to be assessed during the O2C process. This may include surveys to identify other portals that they may use which offer better prices, resolve disputes quickly, have smooth invoicing, billing, and cash applications. This is done so that solutions can be improved and made to be at par, or better than those offered offered by competitors
- Sketching Out the Solution:
ii. Solution: Exploring the possible solutions for identified problems (without finalizing the solution though) for instance, using ML an IR to convert email and portal data into remittance advice or using macros and RPA for it, all solutions should be listed down; All the solutions should be checked with AR analysts for feedback and stakeholder alignment
- Prioritization: The prioritization can be done by assessing the solutions based on the following six indicators.
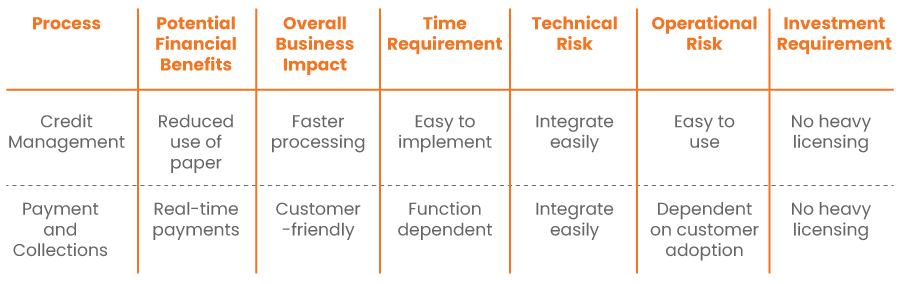
For instance, to assess the priority of implementing online credit application in credit management, electronic presentment, and payment in Payment Portal, the assessment can be carried out as follows:
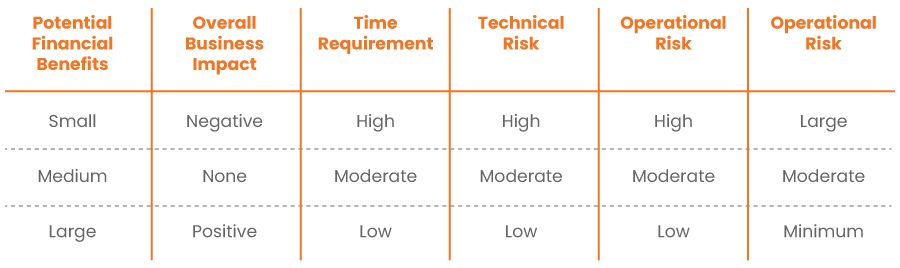
- Roadmap: This step would involve building of value (in terms of customer experience, operation efficiency, and business value) cost, and timelines driven implementation roadmap for prioritized initiatives in the last section. The key consideration while building the roadmap should include:
- Building a Business Case: Defining the business value for each transformation proposed, E.g. reduction in the overall expenditure of AR operations, increase in credit collection rate, and financial value generated
- Setting-up a baseline implementation roadmap which can be refined, based on modified priorities and progress after step 6 and the sequencing of projects for implementation should be done based on the analysis done in step 4
- Solution Implementation: Solutions should be implemented and tested using an iterative approach. The KPIs defined in the first step would help in tracking the progress at this step. Additional indicators, such as the number of successful transactions or the percentage of customers paying electronically for payment can also be tracked based on the solution implemented. Also, O2C process owners should ensure the conduct of weekly and monthly meetings for continuous feedback and stakeholder alignment
Case Study: P&G's GBS Transformation Story
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is a multinational FMCG conglomerate, having several business units. Leaders at P&G wanted to transform the corporation with the large-scale application of digital technology and advanced analytics across every aspect of the company’s operations and activities. P&G’s goal was to carry out an end-to-end digital transformation across the entire organization to achieve efficiency and productivity, and generate maximum business value. P&G aimed for a holistic digital transformation from two perspectives:
- Customer-focused, by improving process reliability
- Operation-focused, by increasing productivity and operational safety
Gap Assessment
P&G first broke down the end objective into achievable business goals. The key challenge was inefficient use of data and redundant data handling systems. The technicians at P&G were often tasked with re-entering the same data across multiple systems. P&G needed an integrated and synchronized system that would enable easy interaction with real-time data. Also, to increase the process reliability and operational safety, P&G needed visibility across the whole supply chain
Ideation
While ideating the right solution, P&G ensured the stakeholder alignment. The major sources of interactions included:
- Customer feedback through its in-house portal, Consumer Pulse, which uses the Bayesian analysis to scan the universe of comments, categorizes them by individual brands, and then puts them on the screen of the relevant individual in P&G
Team feedback through weekly meetings with its leadership team all over the world
Solution Identification, Prioritization, and Roadmap
Based on the gap analysis and feedback received, P&G identified broad areas where it needed transformation and laid out the possible solutions for it. A cluster of solutions include:
- Getting real-time insights across the entire supply chain by placing systems in manufacturing plants to use iPads to download data off the production line in real-time and communicate that to the location where it is rolled up
- Digitizing entire operations, from manufacturing plants, to stores where products are purchased by consumers. Being digitally connected with retailers who support GDSN and have standardized data warehouses so that operations with retail partners can be automated
- Digitizing innovation in R&D using a simulation model to assess consumer feedback on particular products
- Methods to improve data quality by identifying constraints in them and other problems that arise from where they originate
- Building a digital workforce to drive the organization-wide culture and change management, by hiring people with the relevant skills in computer modeling and simulation. P&G also established a baseline digital-skills’ inventory, tailored for each level of advancement in the organization, thereby creating a training facility to make employees competent that pertain to their area or working
Solution Implementation
After the implementation of the solution, P&G put in place indicators to continuously track the progress of the transformation. Some examples of the tracking include:
- Placing a ‘cockpit’ interface on the computers of employees with a certain tolerance for the metrics that are important to their sector. When employees step outside those tolerances, either negatively or positively, an alarm goes off. Analysts can then follow up on it, understand what is going on, and react to it, instantly
- Monday morning meetings to review the business for the previous week and click down on all the data that had been collected from the systems during the previous week
During the whole digital transformation journey, measured it digital transformation journey through business outcome and KPIs. P&G has achieved a partially-synchronized state and is successfully moving toward becoming fully synchronized. In terms of visibility, it envisions a system in place where one can directly see any product at any moment as it goes through the manufacturing line, along with the cost of the product at each stage of its journey. It is working to integrate its operational system with the financial system to achieve true real-time visibility across all functions.
In some cases, the end-to-end transformation may not be the best option for improving existing processes. Even in such cases, the processes of assessment and implementation remain the same. For example, P&G was struggling with high travel expenses and wanted to find a solution that could identify the root cause of the issue and provide its resolution. It first conducted a gap analysis, asking the right questions to identify the information that it would need to analyze the expenses, the types of solutions that would help it resolve the issue, and the cost-benefit analysis of these solutions.
This helped the SSC realize that while the optimization of travel expenses was certainly needed, an end-to-end transformation of the expense management process may perhaps be unnecessary. A thorough analysis and a stakeholder’s feedback revealed that all the relevant data on financial transactions is directly available through credit card companies. P&G just needed to build a policy to leverage that data in an optimal manner to generate insights to reduce the travel expenses. By leveraging existing analysis technologies and datasets, P&G decided to remove the travel management system completely and instead, set up travel-related policies, such as the maximum amount per trip without further checks.
For its implementation, P&G chose a phased approach, to be able to measure the outcomes of new policies by defining suitable indicators. To achieve this, instead of applying these changes across the organization, P&G started with a pilot in the UK. P&G was able to register a 30% reduction in costs for business trips – from a total travel budget of USD 400 Mn – without end-to-end transformation.
The above eBook was just a glimpse out of an extensive Thought Leadership Whitepaper titled:
Future of Shared Service Centers for Order-to-Cash
Key Highlights of the Whitepaper
- SSCs for O2C have evolved to become a part of the core business operations and play a critical role in the overall digital transformation of businesses.
- 70% of digital transformations fail due to lack of discipline, visibility and tracking of business outcomes and KPIs.
- The best-in-class approach includes adopting digitization as a part of the DNA with continuous improvement and benchmarking.
- RPA was good while it lasted but the next generation technology is AI-native.
- Cloud-based integrated O2C platforms are digitally transforming SSCs.





