Key Takeaways
- Learn the significance of the yield curve and how to interpret its various shapes.
- Understand the role of the yield curve in 2023 and what it says about the current economy.
- Get insights into the best practices to safeguard your business against a possible recession.
- Understand the role of Treasury software in Treasury in recession-proofing your business.

Introduction
Not every day you hear people talk about the Treasury yield curve. So when the yield curve does make headlines, it’s generally because it’s setting off some alarm bells among market watchers.
This curve, constructed from the yields of government securities with varying maturities, holds the power to forecast economic shifts, predict interest rate trends, and guide critical financial decisions. Lately, there has been a lot of buzz about the treasury yield curve and how it points towards a possible upcoming recession.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the depths of the yield curve, its role in foreseeing economic downturns, and strategies for businesses to not only weather an unfolding recession but thrive in its midst.
What Is a Treasury Yield Curve?
According to the Federal Reserves, The yield curve, also called the term structure of interest rates, refers to the relationship between the remaining time-to-maturity of debt securities and the yield on those securities.
Yield curves have many practical uses, including pricing of various fixed-income securities, and are closely watched by market participants and policymakers alike for potential clues about the market’s perception of the path of the policy rate and the macroeconomic outlook.
Interpreting the shape of the yield curve
The curve can assume three primary shapes: normal, inverted, and flat. Each shape conveys distinct economic signals, offering corporate financial professionals a glimpse into potential shifts in the business cycle.
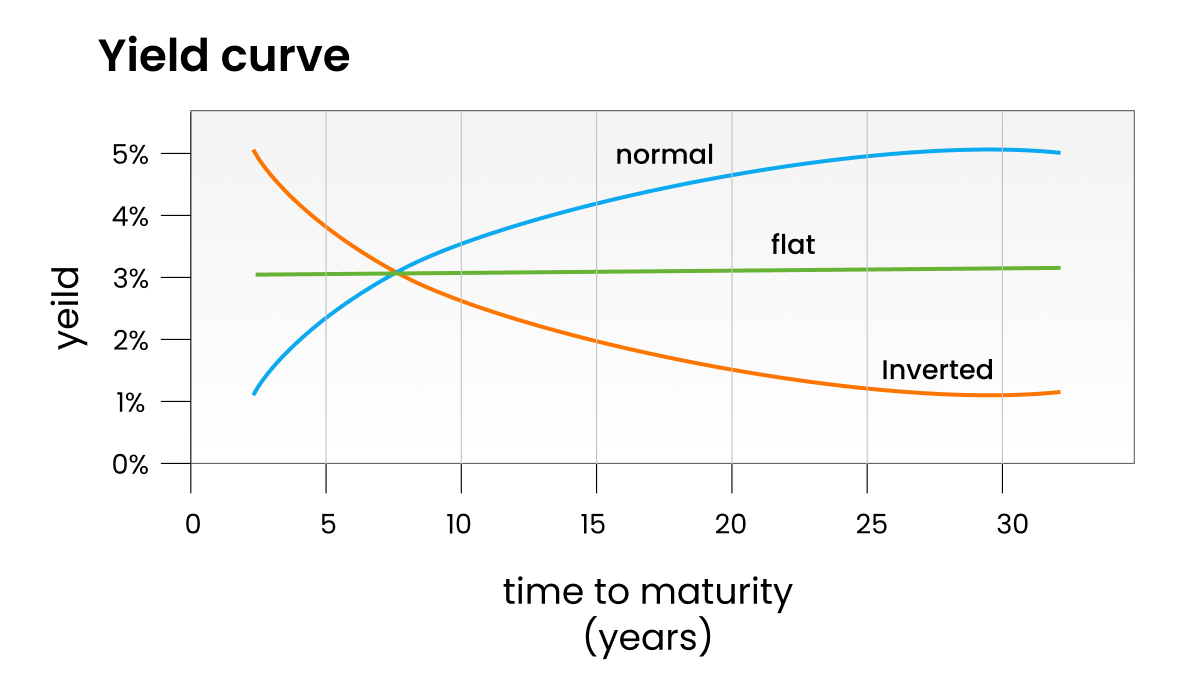
Normal Yield Curve: In this scenario, long-term interest rates are higher than short-term rates. This suggests that the economy is expected to grow, with investors demanding higher returns for locking in their investments for longer periods.
Inverted Yield Curve: An inverted yield curve occurs when short-term interest rates surpass long-term rates. This inversion often portends an economic slowdown or recession. Investors flock to long-term bonds as they anticipate lower interest rates in the future due to potential economic turmoil.
Flat Yield Curve: A flat yield curve emerges when short and long-term rates are relatively similar. This situation typically arises during transitional periods in the economic cycle, indicating uncertainty about future economic conditions.
|
Yield Curve Shape |
Economic Implication |
Potential Strategies |
|
Normal |
Economic growth |
Invest in growth |
|
Inverted |
Recession warning |
Reduce risk exposure |
|
Flat |
Economic uncertainty |
Diversify portfolio |
What does the yield curve in 2023 tell us?
In 2023, the yield curve hit its lowest level since 1981 and the curve is “inverted.” In general terms, that means short-term bonds are paying higher interest rates than long-term bonds.
As of August 10, 2023, the yield on the 3-month Treasury bill was 5.54% while the 2-year Treasury note closed at 4.82%. By comparison, the yield on the much longer-term 10-year U.S. Treasury note was lower, yielding just 4.09%. (source: usbank.com)
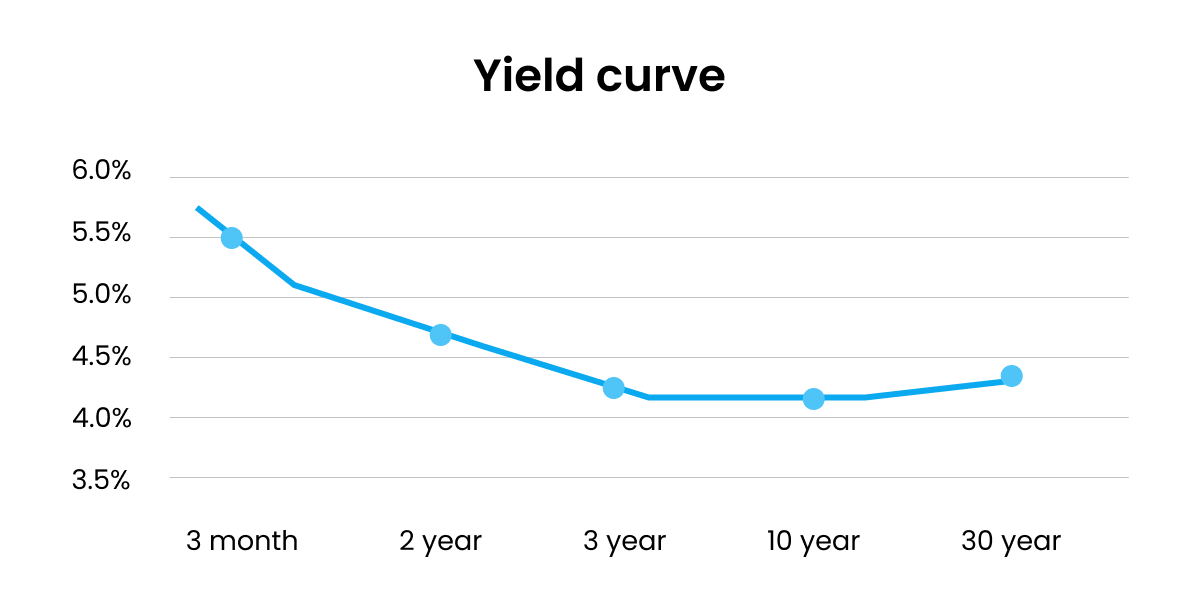
So what does that mean? An inverted yield curve is a classic signal that a recession is on the horizon.
“In fact, since 1978, the yield curve has inverted six times (not counting the current inversion period) and has preceded a recession each time,” Megan Horneman, chief investment officer at Verdence Capital Advisors, wrote in a recent note.
So, why has the yield curve inverted?
Short-term bonds are like loans that the government gives to people for a short time. The government decides how much interest (extra money) it will pay to those who lend them money through these bonds. The Federal Reserve manages the country’s money and sets an interest rate guide. Lately, they raised this rate from 5% to 5.5% to control prices from going up too fast (inflation).
This increase in interest rates caused some investors to become nervous about the economy. They worry that because the Federal Reserve is raising the interest so much, the economy might slow down a lot and even go into a recession. Now, when this happens, investors usually like to put their money in a very safe place. And, nothing is as safe as government bonds.
So, in the current situation, because a lot of people are buying these long-term government bonds, their prices went up, and this made the interest they pay (yields) go down causing an inverted yield curve.
What does an inverted yield curve mean for Businesses?
Historically, an inverted yield curve has often been associated with impending economic slowdowns or even recessions. While the relationship between the yield curve and economic outcomes is not foolproof, it has been a reliable indicator in the past.
For Treasury departments, particularly treasurers and financial managers, understanding and monitoring the yield curve can offer several benefits in terms of future financial planning and risk management. Here’s how an inverted yield curve can help businesses prepare for the future:
-
Early Warning Signal: An inverted yield curve can act as an early warning signal of potential economic challenges. Businesses can use this signal to proactively adjust their strategies and financial plans and make informed decisions about their investments, expansion plans, and hiring practices.
-
Interest Rate Insights: The yield curve reveals market expectations of lower future interest rates. Businesses can take advantage of this insight by considering options to refinance existing debt or secure financing at more favorable terms before interest rates decline further.
-
Cash Management and Liquidity: The possibility of reduced economic activity and tighter credit conditions can impact cash flow. Armed with this information, businesses can build cash buffers, adjust credit policies, and manage their working capital more efficiently.
-
Scenario Planning: An inverted yield curve encourages businesses to engage in scenario planning. By considering various economic scenarios associated with yield curve inversion, businesses can evaluate the potential impacts on their revenue, expenses, and overall financial health.
-
Long-Term Financing Strategy: Inverted yield curves often result in lower long-term interest rates. Businesses looking to invest in long-term projects or expansion can benefit from locking in favorable financing rates during such periods.
How to safeguard your business against a possible recession?
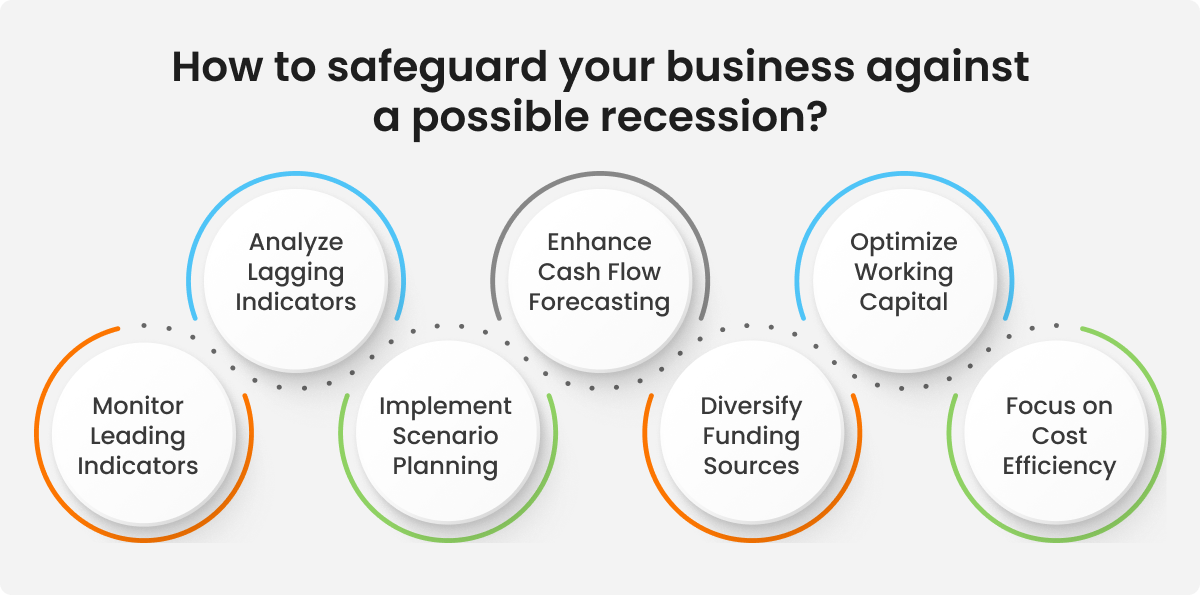
Accurate monitoring, management, and forecasting of cash flows play a pivotal role in safeguarding businesses from a possible recession.
Here are some of the best practices to follow.
-
Monitor Leading Indicators: Stay vigilant for leading indicators of an economic slowdown, such as changes in payment terms, customer credit scores, or delayed payments. These early warning signs can help you prepare for potential cash flow challenges.
-
Analyze Lagging Indicators: Examine lagging indicators like past-due accounts receivable to gauge your organization’s financial health. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of your credit and collection strategies.
-
Implement Scenario Planning: Create various financial scenarios to assess the potential impact of different economic conditions. This proactive approach helps you formulate contingency plans and make informed decisions in response to changing market dynamics.
-
Enhance Cash Flow Forecasting: Regularly update and improve your cash flow forecasts using historical and current data. This ensures accurate predictions and allows you to anticipate cash shortfalls or surpluses, enabling timely adjustments.
-
Diversify Funding Sources: Reduce dependence on a single funding source. Diversify your financing options, including short-term and long-term debt, equity, and credit lines, to maintain financial flexibility during periods of uncertainty.
-
Optimize Working Capital: Efficiently manage working capital by optimizing inventory levels, managing accounts payable and receivable, and controlling operating expenses. This can help improve liquidity and mitigate cash flow challenges.
-
Focus on Cost Efficiency: Evaluate and reduce non-essential costs to enhance your organization’s resilience against financial pressures. Implement cost-saving measures while maintaining essential business functions.
Can Treasury automation recession-proof your business?
Treasury automation is one of the most powerful ways to recession-proof a business. By focusing on cash management and forecasting, businesses can stay strong even during tough times.
At HighRadius we help businesses transform their Treasury Landscape. Our Treasury software helps businesses make better daily cash decisions by automating their cash management processes. Plus, it helps companies make better borrowing and investing decisions with reliable daily forecasts that are produced in 90% less time.
With experience in more than 800+ digital transformation projects, we promise to give your team the extra edge needed to not just survive but thrive during a recession. Wish to learn more? Check out HighRadius’ Autonomous Treasury Software.
FAQs on the Treasury Yield Curve
1. How do you interpret a yield curve?
The yield curve depicts interest rates for various maturities. A normal curve slopes upward, showing higher rates for longer terms. Inverted means shorter-term rates exceed longer-term rates, suggesting economic uncertainty. Steepening or flattening reflects market expectations about future economic conditions.
2. What affects the yield curve?
The yield curve is influenced by economic factors like interest rates, inflation expectations, and market sentiment. Short-term rates typically mirror central bank policies, while long-term rates reflect future economic conditions and investor perceptions, leading to various curve shapes (e.g., upward-sloping, flat, or inverted).
3. What happens when the yield curve goes negative?
A negative yield curve, with short-term interest rates higher than long-term rates, often predicts economic uncertainty, potential recession, and reduced lending. Investors seek safety, impacting borrowing costs and potentially stalling economic growth.








