Break the siloes in your Order to Cash process with end-to-end receivables automation
As evident from the name, blockchain is a chain of blocks, where each block consists of transaction data and is connected to its previous block. Blockchain as a technology operates on two fundamental concepts:
Distributed ledger
It is a shared, distributed ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking cash flow in a business network. Through this ledger, an immutable record of all transactions is present on the blockchain for all participants to access.
Smart contracts
It is a set of computer instruction (code) that all the participants must agree. This code acts as a trigger which on successful validation of data, is converted into a block and written into the blockchain.
How blockchain fills the gaps in A/R processes
Accounts receivable accruals automation
For A/R accruals, following proper accounting standards requires periodic auditing, keeping track of payments received, and allocating them in either of receivables, liability or revenue. For tracking hundreds of A/R accruals, the process is time taking, cumbersome, and prone to errors.

Smart contractsenable real-time reconciliation of A/R accruals for both suppliers and buyers by getting triggered at each stage of service completion, eliminating the need for accountants to record individual transactions but rather monitor them.
Reducing deductions
Deductions are a common occurrence for CPG, Food & Beverage and Apparel industries arising out of reasons such as discounts, damaged goods, late deliveries. For CPG giants such as Walmart, it results in hard to resolve conflicts with suppliers.
Chief Product Officer at HighRadius, Sayid Shabeer, explains:
“Conflict resolution often gets delayed because of restricted access to data owned by different stakeholders. For example, stakeholders from different departments among both suppliers and customers (Walmart), logistics providers, auditors, as well as issues related to traceability of related transactions and documents.“
Blockchain technology provides the much-needed level of transparency required to avoid these conflicts from happening. Or, simply resolve them in an automated manner, without complications.
Shabeer continues, “Walmart could, for example, host a blockchain for trucking companies so that both suppliers and Walmart could use the distributed ledger for reconciliation. The expedited resolution of disputes would benefit both the suppliers and the buyers in relation to AR/AP.”
Pre-approved transactions for faster procure-to-pay cycle
In current A/R processes, different versions of the same invoice are stored in disparate locations such as supplier’s billing system, buyer’s accounting system, supplier side e-invoicing provider’s database, and financial institution records. Each invoice copy gets modified independently from each other, making it inconsistent with other versions and leading to inefficiencies across the order-to-cash cycle.
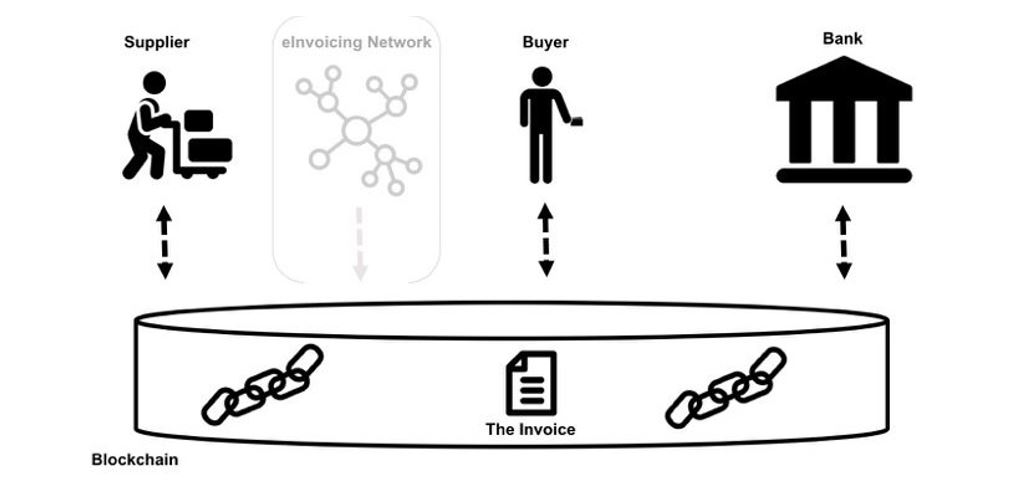
Fig : Blockchain as the single source of truth, Source: Blockchain First, Markus Ament
With a distributed ledger, every participant has access to a single valid document and use it for further processing in their ERP system. Hence there are no inconsistencies with A/R and A/P. The buyer could also embed remittance details into the blockchain which everyone can access.
“Buyer generated purchase order and supplier received sales order is the same blockchain”
This eliminates the need to
All this results in accelerated settlements and improved cash flow.
Increased trust among stakeholders through centralized credit information accessibility
Blockchain technology would help increase trust among clients and vendors through easy access to buyer credit score across the supplier community based on buyer payment behavior, purchase history, the validity of deductions claimed. The accumulated and stored history of transactions would help build trust and transparency among stakeholders.
“Distributed credit information accessibility leads to swift distribution of authentication rights”
With the recent hype over multiple use-cases for blockchain, it is difficult for executives to zero-in on a decision. But unless the core transaction management of your A/R processes is streamlined, blockchain will not solve your challenges and will fall short of delivering its promised potential. Before applying blockchain to your A/R processes, there are a few questions that you need to ask yourself.
All the manual A/R processes such as chasing transactions, fetching backup documents, preparing invoices, posting cash need to automated by using technology such as RPA and Artificial Intelligence. Technology would be able to mimic analyst activity and free up their bandwidth from doing low-value tasks resulting in speed, cost savings, and reduced errors.
“Blockchain is NOT automation. AR processes need to have ‘true’ automation in place for blockchain to show results”
To optimize the end-to-end A/R process, efficient data exchange needs to take place between different A/R processes such as deductions, collections, credit, cash application for better transparency. Cloud automation helps to establish a single source of truth for seamless information exchange across processes. This concept is called Integrated Receivables where each process ‘communicates’ with other A/R processes instead of operating in silos.
“To realize the speed and transparency benefits of blockchain, your AR processes need to transform from siloed functioning to Integrated Receivables“
Before embarking on adopting blockchain for optimizing your A/R process, it is important to balance the benefits of blockchain with the cost of integrating this technology into existing systems such as validation workflows, accounting systems, and the cost to address cybersecurity. A winning business case should address what will be saved or increased from implementing the system.
“Having realistic numbers for before and after is necessary to understand what the system will do for you and from where your savings and optimization will come“

Leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation to reduce repetitive and time consuming tasks of accounts receivable process
Get on a demo call