Chapter
01
Why is managing risks a top priority for treasury execs?
Over the past years, the types and quantity of business risks that might impact a company’s treasury risk management have multiplied due to the rapid rate of change brought on by digital innovations and the developing regulatory environment.
Treasury leaders manage several key risks related to changes in interest rates, credit, currency, commodities, and operations. Businesses may be exposed to any or all of these risks. The most common risks include:
The 5 most common risks include:
- Liquidity risk: Liquidity risk refers to the risks of a company running out of cash due to insufficient sales, excessive spending, or the inability to obtain financing from banks and other outside sources.
Examples: funding liquidity/cash flow risk, and market liquidity risk.
Role of CFOs in managing liquidity risks:
CFOs have difficulty locating suitable cash repositories to meet their liquidity demands. A liquidity crisis can arise when multiple financial institutions face a liquidity crunch and start withdrawing their self-financed reserves or trying to sell assets to generate cash. The CFO should continually examine the company’s cash flow situation and forecasts to prevent being caught with a sudden shortage.
- Credit risk: Credit risk is the likelihood of suffering a loss due to a borrower’s failure to make payments on any debt.
Examples: sovereign risk and settlement risk.
Role of CFOs in managing credit risks:
The CFO must ensure that those issuing or insuring securities are financially stable and creditworthy if surplus funds are to be invested to earn interest. Checking an issuer’s credit rating, which offers an unbiased assessment of the possibility that a third party will pay on time and in full as anticipated, is one approach to do this. The CFO must also be confident that counterparties to financial instruments that manage risks (such as interest rate swaps) will perform as expected.
- Interest rate risk: Interest rate risk is the probability of a decline in the value of an asset resulting from unexpected fluctuations in interest rates.
Examples: repricing risk, yield curve risk, basis risk, and option risk.
Role of CFOs in managing interest rate risks:
CFOs are also working to hedge against interest rate risk. Reducing the effect of uncertainty related to interest expenses and unfavorable movements in interest rates through hedging makes cash flow more predictable and can help protect a business’s profitability.
- Foreign exchange risk: Foreign exchange risk refers to the risk of a company losing money due to currency changes in foreign financial transactions.
Examples: transaction risk, economic risk, and translation risk.
Role of CFOs in managing foreign exchange risks:
An FX risk framework’s success relies on identifying weaknesses, both internally and in the markets. Yet because of the unstable nature of FX rates, volatility and hedging, corporations struggle to spot the risks. The need to protect revenues from multi currency volatility and costly hedging forces CFOs to develop intelligent solutions for FX risk management. CFOs can enable corporate treasury teams to make smarter decisions by enhancing how FX rates are obtained and risk is evaluated.
- Operational risk: Operational risk in treasury management refers to the risks and uncertainties that a corporation encounters when doing day-to-day business activities in a certain area or industry.
Examples: process risks, compliance risks, supply chain risks, and personnel risks.
Role of CFOs in managing operational risks:
According to a new survey from FM Global, most CFOs claim that their companies have faced various operational risks over the previous years.
The organization must consider its goals and treasury risk management functions while managing operational risk. Since operational risk is pervasive, the goal is to reduce and control all risks to an acceptable level.
Although CFOs are used to managing these risks, the looming combination of rising interest rates and inflation creates significant uncertainty over the short and long terms in treasury risk management. Any one of these risks may limit a business’s potential for expansion. CFOs can employ advanced financial modeling to identify risks and business possibilities for their companies. Additionally, CFOs can use technology to ensure information visibility and accessibility throughout the company.
Chapter
02
How does technology help in risk management? What are the best practices for managing risks?
Automated treasury technology, with real-time data collection, processing, and monitoring, will be able to flag potential threats sooner than is currently possible, giving CFOs more time to focus on evaluating the identified threat and curtailing it before it reaches its target.
The three major areas where technology can enhance treasury risk management functions are:

- Data: While new internal and external data sources are flooding in at an unprecedented rate, organizations must invest significantly to generate deeper insights from historical data while also preparing their risk processes to benefit from new sources.
- Analytics: Analytics and big data can help with treasury management tasks in various areas, including asset and liability management, compliance, interest rate and foreign exchange (FX) risk hedging, cash management, and compliance. This will significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of fraud detection, debt collection, conduct monitoring forensics, and customer support.
- Processing: Effective processing, clean workflows, and a clear understanding of your goals are the foundation of successful technology deployment. Digitization allows for the automation and development of new risk-monitoring processes for managing emerging or hidden risks.
What are the best practices for managing risks?
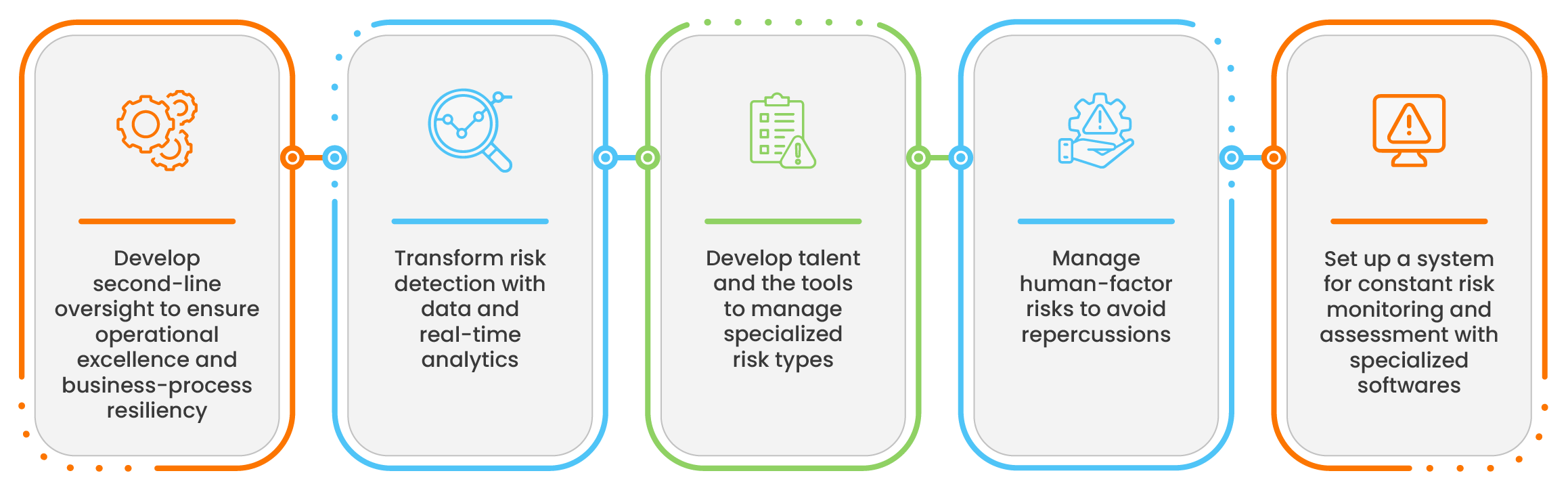
The best practices you can implement to manage risks are:

Even though these best practices help an organization greatly, AI-powered treasury management software helps safeguard your organization against unforeseen risks and human errors.
Below are the unique features HighRadius Cash Forecasting software provides, which can help with treasury risk management.
Chapter
03
Next-gen treasury risk management with HighRadius cash forecasting software
CFOs should adopt AI-based cash flow forecasting software to serve as strategic advisors for their companies. The benefits of adopting the HighRadius cash forecasting software for minimizing treasury risks are:
- Tailor forecast models: The cloud-based cash forecasting solution has an intuitive spreadsheet interface with formula or manual data entry that enables users to create their own models or customize pre-existing ones.
- Customize forecasts for different timelines: The HighRadius cash flow forecasting software helps treasurers adjust time horizons to create forecasts according to their needs. However, during volatile situations, treasurers should perform weekly or regular cash flow projections to have end-to-end visibility of current and historical data. This enables them to take corrective action, such as enhancing payment and collection methods, selling assets, or approaching lenders.
- Perform real-time scenario analysis: CFOs and treasurers should manage a variety of scenarios, evaluate actions, and predict potential outcomes and effects using scenario planning. The cash forecasting software assists CFOs in making better decisions by examining the risks and rewards of various options through accurate stress-testing of best and worst-case scenarios, factoring in unexpected events, and planning future cash flows.
- Generate highly accurate cash forecasts: The treasury management software improves the accuracy of the forecasts through machine learning by comparing past and recent results, identifying errors, and making continuous improvements.
Treasury can drill down to deviations between forecasts and actuals. This helps treasurers to understand the root causes of variance and use corrective measures to improve the accuracy of cash forecasts over time.
HighRadius helped HNTB, a construction company, increase their forecast accuracy by 94% in high-variance cash flow categories with HighRadius Cash Forecasting Software.
Watch this product tour now to see how to analyze, identify and improve treasury risk management using the HighRadius treasury management software.